What is Skin Cancer?
The quick answer is that skin cancer is the abnormal and rapid growth of skin cells. However, there’s a lot more to it than people think. It occurs when the body does not repair the damage to the DNA inside skin cells, which allows the cells to divide and then grow uncontrollably. Skin cell damage can be caused by a number of factors such as genetics or skin type. Most cases, however, are caused by overexposure to damaging rays produced by the sun.
The type of skin cancer depends on the cells that are damaged. There are three types:
While it’s not the most common, Basal Cell Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and more common in young people. A unique characteristic of melanoma is its ability to spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma cancer symptoms are bumps or patches that resemble moles. They are usually black or brown, but can also be blue, red, pink, white, or even skin colored. Although dangerous, if recognized and treated early, melanoma can be cured.
The most common form of skin cancer is Basal Cell Carcinoma, which occurs in the outer layer of your skin. This form is not as likely as other skin cancers to metastasize (spread) to other parts of the body. Symptoms often include open sores that won’t heal, dark or red patches, or shiny pimple-like bumps or scars. People with dark hair or skin tone will often show skin cancer signs that have a darker color to the lesion or patch on their skin.
The second most common type of skin cancer, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, occurs when abnormal cells start to grow in the upper layers of the skin. Symptoms most commonly appear on parts of the body frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, ears, lips, and neck. Symptoms include open sores; wart-like bumps; scaly red patches; and a sore with raised edges with a central hole, often referred to as the “rat bite” tumor due to its distinctive appearance.
Cancer Staging:
Ranging 0 through 4, the cancer stage depends on factors like whether or not the cancer has localized, how far/if the cancer has spread, and the size of the tumor. At stage 0, the cancer is still confined to the tumor. Each stage beyond this indicates an increase in size and how far the cancer has spread. Stage 4, the final stage, is the point where the cancer has spread to most of the body and has become very difficult to treat.
*There are also different factors with staging skin cancer, such as whether or not the cancer appears on the eyelids (the most common site for skin cancer) and whether or not it is non-melanoma or melanoma.
Symptoms, the ABCDE’s of Skin Cancer:
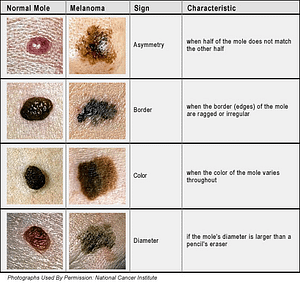
Asymmetry: Draw an imaginary line through the middle of the mole or lesion on your skin and if the two halves are not symmetrical (they don’t match), this may be a sign that it’s malignant.
Border: Non-malignant moles usually have a smooth, regular border. The border of an early melanoma will generally be jagged or uneven.
Color: Melanomas are known for being a variety of colors, particularly shades of black, brown, and tan. They may also be blue, red, and other colors. A non-malignant mole or growth is normally one color.
Diameter: Non-malignant skin cancers are usually smaller than a quarter inch in diameter. Melanomas, on the other hand, are usually larger in diameter.
Evolving: Potential skin cancer symptoms include changes in color, elevation, size and shape of the mole, or issues like bleeding, crusting, itching, etc.
*Not all cancers fit the ABCDE profiling. It’s important to stay alert and consult with your physician about any out of the ordinary spots and growths, or any freckles and moles that seem unusual.
Who’s at Risk?
Everyone. EV-ER-Y-ONE. Do not let the it-doesn’t-run-in-my-family/ I-never-burn myths deter you from paying attention and being aware of what to look for. Yes, you can get skin cancer. YES.
Now that we have that out of the way, some people are predisposed for a number of reasons.
- People with freckles
- People with fair skin
- Those who burn easily
- People with light colored eyes, like green and blue eyes
- People with naturally red or blonde hair
- Age – basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer risk increase with age, whereas melanoma often occurs in younger people
- People with a lot of moles, especially those with abnormal moles
- People who are post radiation treatment
- People with a weakened immune system
- People who consume alcohol
- People who smoke
- People with poor diets
- People who do not get enough Vitamin D
- People with certain viruses and bacteria
- People who are exposed to environmental toxins and chemicals
Sunscreen:
I used to be the mom who trained her kids to stop, spread their arms, and close their eyes so I could lather them up with sunscreen before releasing them to the water. As they sprinted through the sand, I’m sure I even breathed a sigh of relief as I sank into my chair and opened my book. I guess it never occurred to me to ask myself later why my youngest son broke out into a rash each time. It was just something that happened. Better than cancer, right? Ugh.
 What I know now: Here in the US, the government does not regulate sunscreen. As is the same for supplements, we think we’re doing something good for our health just to find out that we’re actually making it worse. My process for choosing a good sunscreen consisted of two qualifications: price and spf. I never considered turning the bottle over to look at the ingredients. What would I be looking for, anyway? I know that now, too. Here’s what you DON’T want: Oxybenzone – this is a hormone disrupting chemical that penetrates the skin and enters the bloodstream. It is the most popular ingredient in chemical-based sunscreens and only blocks UVB ray (sun’s good rays that provide vitamin D production), and not UVA which are the most free radical damaging rays. Avoid any sunscreen that has this chemical at all costs, especially for children (Foodbabe). Now, here’s what you DO want: Look for titanium dioxide and zinc oxide based mineral sunscreens, which don’t penetrate the skin and provide UVA protection against the sun’s most damaging rays (Foodbabe).
What I know now: Here in the US, the government does not regulate sunscreen. As is the same for supplements, we think we’re doing something good for our health just to find out that we’re actually making it worse. My process for choosing a good sunscreen consisted of two qualifications: price and spf. I never considered turning the bottle over to look at the ingredients. What would I be looking for, anyway? I know that now, too. Here’s what you DON’T want: Oxybenzone – this is a hormone disrupting chemical that penetrates the skin and enters the bloodstream. It is the most popular ingredient in chemical-based sunscreens and only blocks UVB ray (sun’s good rays that provide vitamin D production), and not UVA which are the most free radical damaging rays. Avoid any sunscreen that has this chemical at all costs, especially for children (Foodbabe). Now, here’s what you DO want: Look for titanium dioxide and zinc oxide based mineral sunscreens, which don’t penetrate the skin and provide UVA protection against the sun’s most damaging rays (Foodbabe).
Conventional Treatment:
There are many factors that determine what kind of treatment is best for skin cancer, such as non-melanoma/melanoma, stage, type, and the patients’ age and overall health. Treatment could come in the form of surgery to remove the tumor or the cancer that has spread. Radiation therapy destroys or shrinks the tumor, but it can cause side effects such as skin irritation and/or vomiting and hair loss. Chemotherapy (“chemo”) uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. Unfortunately, it’s also highly toxic and causes side effects like nausea, vomiting, and hair loss. Even worse, it’s not selective to just cancer cells; it can also kill healthy cells.
Lifestyle Changes for Skin Cancer Prevention and Symptoms:
- The most important prevention is done by keeping your body clear of any toxins. There are a number of ways to do that, starting with keeping your physical, mental, and emotional health in balance. You can do this by simply getting outside, breathing in the fresh air, going for a walk or exercising. Be sure to do this in a safe way as to not aggravate any symptoms. Take precautions by wearing a hat, sunglasses, and a titanium dioxide or zinc oxide based mineral sunscreen.
- Filter your water to remove any chemicals like chloride, fluoride, and arsenic.
- Use natural or organic cleaning products that do not contain dangerous chemicals.
- Do a detox every six months, like a liver cleanse to balance your digestive tract and to help rid your body of any existing irritants.
- Include cancer-fighting foods in your diet, such as healthy proteins like grass-fed beef, eggs, wild-caught fish, nuts and seeds; green leafy vegetables, like kale and spinach, that are rich in essential minerals, vitamins, and fiber; healthy fats like avocados, nuts, olive oil, coconut oil, or ghee; and antioxidant-rich foods like berries, pecans, walnuts, cloves, artichoke hearts, acai berries, and garlic.

Supplements to Help Skin Cancer Symptoms:
- Vitamin D is critical to your health, as well as your immune function.
- Probiotics help boost healthy bacteria in the gut, and aid in stronger immune function and improve digestion.
- Turmeric has many health benefits, including boosting immune health and potentially helping to treat cancer.
Final Thoughts…
Be sure to learn the ABCDEs when examining any suspicious moles or growths so that you can be aware of what to look for. If you see anything that seems abnormal, contact your doctor right away. Skin cancer is diagnosed through a combination of examinations and biopsy. There are three main types of cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Treatment depends on the staging of the cancer/how advanced it has become. Skin cancer is treatable and preventable. Natural therapies are available to aid and prevent cancer. Remember to always take precautions, pay attention, and know your body!
Adrian Schirr
Forum Health Clarkston
7300 Dixie Hwy, Suite 500, Clarkston, MI 48346
248-625-5143
Resources:
Cancer Center
Dr. Axe
Foodbabe







